Vision AI, a subfield of artificial intelligence, enables machines to interpret and analyze visual data such as images and videos. Powered by advanced computer vision and machine learning technologies, Vision AI leverages neural networks and deep learning to recognize objects, extract actionable insights, and process visual content. Businesses across industries are using Vision AI to enhance decision-making, automate tasks, and provide cutting-edge solutions.
In this article, we explore Vision AI in-depth, including its types, features, and uses, with a focus on keywords such as computer vision, optical character recognition (OCR), image classification, and object detection.
The Core of Vision AI: Computer Vision
Computer vision forms the foundation of Vision AI. It involves training machines to interpret visual inputs like humans do. Through computer vision technology, machines analyze images and extract meaningful patterns, enabling them to perform tasks such as facial recognition, image classification, and optical character recognition (OCR).
The evolution of computer vision applications has been driven by advancements in deep learning and neural networks. These systems are trained on massive datasets to identify patterns, process visual data, and achieve accurate results in real-time.
How Vision AI Works
Vision AI combines several technologies, including:
Image Processing: Enhances raw images to improve quality and clarity.
Machine Learning Models: Enables machines to learn from data and recognize objects or patterns.
Advanced Algorithms: Powers object detection, image analysis, and visual inspection.
Deep Learning: Helps train models to interpret complex visual inputs.
By using these components, Vision AI can analyze images and video data, recognize patterns, and make predictions with unparalleled accuracy.
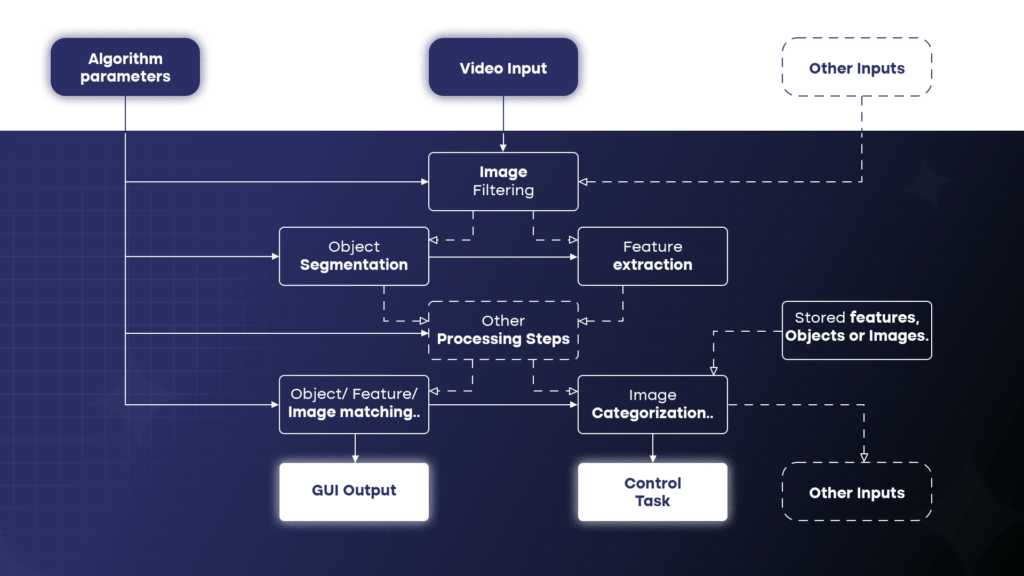
Types of Vision AI
Vision AI encompasses various types, each tailored to specific applications:
Image Classification
Image classification involves assigning labels to images based on their content. For example, Vision AI can identify whether an image contains a car, a cat, or a tree. This is widely used in industries like e-commerce for tagging products or in healthcare for diagnosing medical conditions through visual inputs.
Object Detection and Object
Object detection and object recognition enable Vision AI to identify specific objects within an image or video. This type of AI is used in autonomous vehicles, surveillance, and retail for tracking inventory.
Facial Recognition
Facial recognition systems analyze facial features to identify individuals. This application is widely used in security, personalized marketing, and customer experience management.
This technique divides an image into segments, each representing a different object or region. The Mask R-CNN model is widely used for instance segmentation, enabling detailed understanding of the image content.
Optical Character Recognition (OCR)
Optical character recognition (OCR) extracts text from physical documents and converts it into a digital format. This is crucial for automating data entry, enabling businesses to process handwritten text and printed documents more efficiently.
Image and Video Analysis
Vision AI systems can analyze images and video data to detect anomalies, monitor production lines, and assess compliance with safety protocols.
Features of Vision AI
Vision AI offers a range of features that make it indispensable for businesses:
1. Image and Video Processing
Vision AI excels in image processing, improving clarity and extracting information from visual content. It can process video data in real-time, providing insights for industries like transportation and entertainment.
2. Object Identification and Classification
The ability to identify objects and classify them accurately is a core feature. This includes applications like visual inspection in manufacturing or detecting defects in production lines.
3. OCR and Text Extraction
Optical character recognition (OCR) allows Vision AI to extract text from images, making it easier to digitize physical documents and automate workflows. This is especially useful for legal and financial institutions handling large volumes of customer data.
4. Integration with AI Technologies
Vision AI integrates seamlessly with other AI technologies, such as predictive analytics and voice recognition, to provide holistic solutions for businesses.
5. Neural Network-Powered Insights
By leveraging neural networks, Vision AI systems can recognize patterns in visual data and deliver actionable insights. This helps organizations improve decision-making and optimize their operations.
Classifying Vision AI Based on Hardware
Vision AI applications rely on a variety of hardware platforms, each tailored to meet specific performance, power, and cost requirements. The choice of hardware plays a critical role in the efficiency and effectiveness of Vision AI systems, influencing their ability to process and analyze visual data
CPU-Based Vision AI
CPU-based Vision AI utilizes general-purpose processors designed for a variety of tasks, making them suitable for simple image processing tasks and non-real-time applications. These processors are widely available and affordable, capable of handling other computational tasks alongside Vision AI. However, they offer slower performance compared to specialized hardware for complex vision tasks and have limited parallel processing capabilities. Intel Xeon processors, for example, are often used for basic image processing tasks and can run various Vision AI applications at a lower cost. These processors provide a cost-effective solution for developers and businesses looking to integrate Vision AI without the need for specialized hardware.
GPU-Based Vision AI
GPU-based vision AI leverages specialized processors designed for parallel processing of large datasets, making it ideal for deep learning models and real-time applications. With significantly faster performance for vision tasks, GPUs can efficiently handle complex models and high-resolution images, offering a substantial advantage over traditional CPUs. However, this technology also has its drawbacks, such as higher power consumption and cost, along with the need for specialized programming skills. A popular product example is the NVIDIA Tesla GPU, widely used in data centers and research labs for training deep learning models and conducting real-time image and video analysis.
TPU-Based Vision AI
TPU-based vision AI utilizes application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) designed specifically for machine learning workloads, particularly optimized for neural networks and tensor operations. This specialized hardware provides exceptional performance for deep learning tasks, offering a significant advantage in neural network processing while maintaining lower power consumption compared to GPUs. However, TPUs come with limitations, such as limited availability, higher costs, and the need for specific programming techniques. A prime example is Google’s Tensor Processing Units (TPUs), which are used in Google Cloud to accelerate machine learning workloads, delivering high efficiency for Vision AI tasks.
FPGA-Based Vision AI
FPGA-based vision AI uses reconfigurable hardware that can be programmed to perform specific tasks, making it suitable for custom hardware acceleration and real-time applications. This technology offers flexibility, allowing it to be reconfigured for different tasks, and provides low latency and high performance for specific applications. However, FPGA-based solutions often require specialized programming skills and come with higher development costs, and they may be less efficient for general-purpose vision tasks. A notable example is Xilinx FPGAs, which are widely used in various industries for custom Vision AI applications, delivering high performance and flexibility for tasks such as video processing and real-time analytics.
Edge AI Devices
Edge AI devices are embedded systems with limited computational power, specifically designed for low-power, real-time applications. They provide several advantages, including reduced latency, improved privacy, and the ability to operate offline, making them ideal for scenarios where connectivity is limited or data security is a concern. However, their limited computational power necessitates the use of smaller and more efficient models. An example of a popular edge AI device is the NVIDIA Jetson Nano, TI AM62A, Renesas RZ/V series MPUs, which offers a compact and low-power solution for deploying Vision AI models in the field.
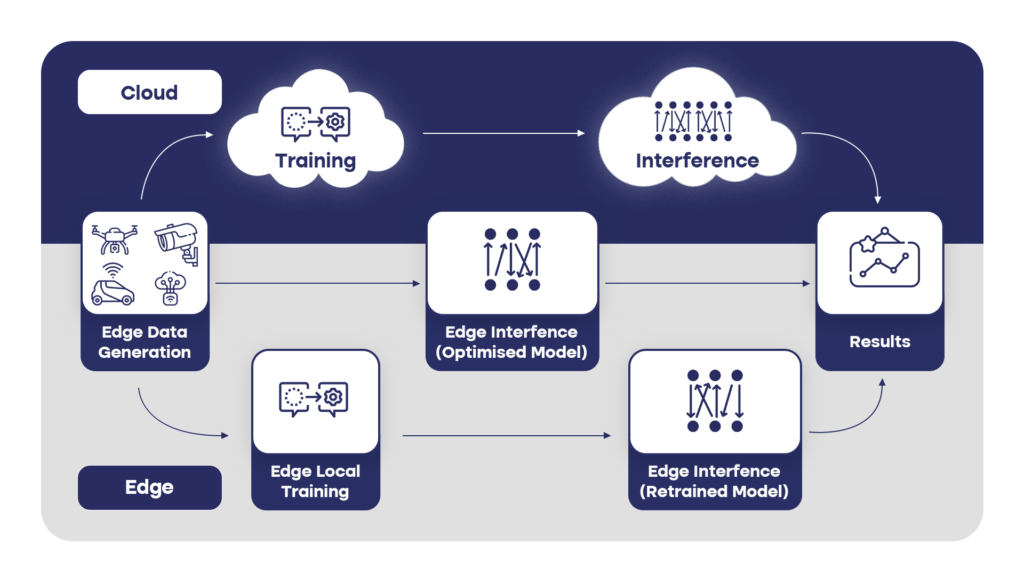
Cloud-Based Vision AI
Cloud-based Vision AI leverages powerful cloud infrastructure to perform complex AI tasks, providing access to large-scale computing resources and scalability to handle increasing workloads. This approach allows developers to integrate advanced Vision AI capabilities into their applications without the need for managing local infrastructure. However, it comes with certain disadvantages, such as increased latency due to network communication and potential privacy concerns associated with storing and processing data in the cloud. A notable example is Amazon Rekognition, a cloud-based service that offers image and video analysis, enabling developers to seamlessly incorporate Vision AI functionalities into their applications.
Use Cases of Vision AI
This transformative impact is evident across a multitude of industries, driving innovation and efficiency in ways previously unimaginable. Its ability to interpret and analyze visual data opens up a broad spectrum of applications, each tailored to address specific needs and challenges. From enhancing healthcare diagnostics and powering autonomous vehicles to optimizing retail experiences and streamlining manufacturing processes, Vision AI is reshaping how we interact with and leverage visual information. Additionally, emerging use cases such as automated image descriptions, real-time video stream processing, and high-precision visual inspections highlight the expanding potential of Vision AI. These diverse applications not only illustrate the versatility but also underscore its growing importance in modern technology and business practices.
Applications of Vision AI
In Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS), Vision AI is crucial for enabling self-driving cars to perceive their surroundings, identifying objects like pedestrians, vehicles, and road signs. Tesla’s Autopilot system exemplifies the use of Vision AI for autonomous driving. AI models also assist in path planning and navigation, ensuring safe and efficient travel, as seen with Waymo’s use of Vision AI to navigate complex urban environments. Furthermore, Vision AI systems enhance safety by detecting and avoiding obstacles in real time, with Mobileye’s technology being widely used in various autonomous vehicles for obstacle detection and avoidance.
Healthcare
Vision AI enables early diagnosis of diseases through medical imaging. Technologies like image classification and deep learning power diagnostic tools that can analyze X-rays and MRIs.

Retail
In retail, Vision AI helps track inventory, enhance the shopping experience, and automate checkout processes using object detection and facial recognition.
Manufacturing
Manufacturers use Vision AI for visual inspection to detect defects on production lines. It also automates quality control and ensures compliance with safety regulations.
Finance
Financial institutions utilize Vision AI to digitize and process documents using optical character recognition (OCR), improving efficiency and reducing manual errors.
Autonomous Vehicles
Self-driving cars rely on Vision AI to interpret road signs, detect obstacles, and navigate safely. Computer vision applications in this domain involve real-time image analysis and decision-making.
Security and Surveillance
Vision AI enhances security systems through facial recognition and object detection, enabling real-time monitoring and threat identification.
Marketing and Advertising
By analyzing visual inputs, Vision AI allows businesses to create targeted marketing campaigns, enhancing customer engagement and satisfaction.

Benefits of Vision AI
Automation: Automates repetitive tasks like document processing and data labeling, saving significant time and effort.
Improved Accuracy: Delivers accurate results by reducing human errors in tasks such as defect detection or image labeling.
Cost Efficiency: Reduces operational costs by automating workflows and improving resource allocation.
Scalability: Vision AI systems can handle large volumes of visual data, making them suitable for enterprises of all sizes.
Enhanced Decision-Making: Provides actionable insights that help businesses make informed decisions based on visual content.
Challenges and Considerations
While Vision AI offers immense potential, its adoption comes with challenges:
Data Privacy: Handling sensitive visual data requires robust security measures to protect user information.
Technical Expertise: Implementing Vision AI solutions often requires specialized knowledge and skills.
Training Models: Developing custom models and training them can be resource-intensive.
Integration: Ensuring that Vision AI systems integrate smoothly with existing tools and workflows can be complex.
Future of Vision AI
The future of Vision AI lies in further advancements in deep learning and neural networks. Emerging technologies like AI vision and augmented reality will open new possibilities for businesses. Additionally, as Vision AI continues to evolve, its applications will expand into areas such as education, entertainment, and environmental conservation.
Businesses can harness the power of Vision AI to unlock new opportunities, enhance productivity, and gain a competitive edge. With its ability to analyze images, process video data, and deliver insights, Vision AI is transforming industries and shaping the future of technology.
By leveraging computer vision technology and integrating it with AI technologies, Vision AI has become a game-changer. From automating processes to improving customer experiences, its applications are limitless. Companies that invest in Vision AI today are paving the way for innovation and success in the digital age.





